
Introduction
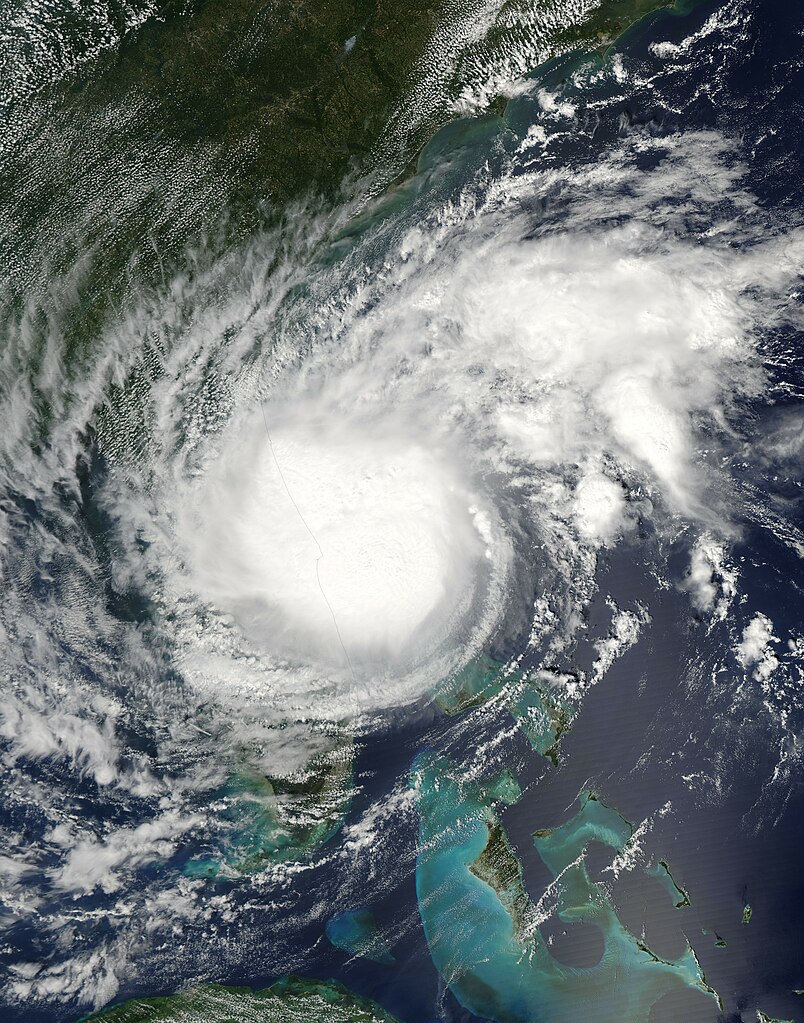
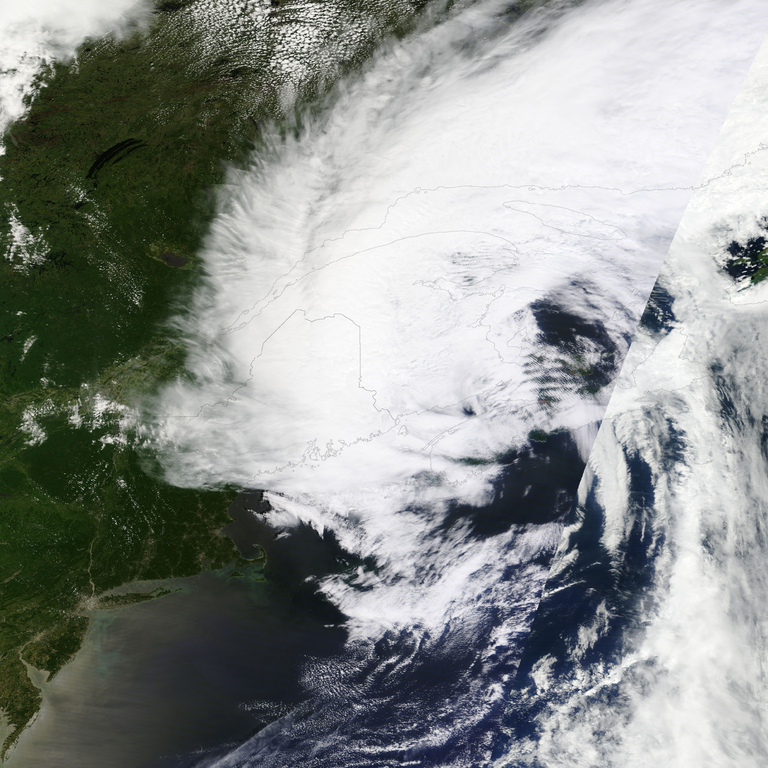
Hurricane Arthur was the first named storm of the 2014 Atlantic hurricane season and made a notable impact on Atlantic Canada in early July. As it transitioned into a post-tropical storm, Arthur brought heavy rainfall and strong winds, particularly affecting Nova Scotia and New Brunswick.
Meteorological History
Arthur began as a tropical storm off the southeastern coast of the United States and quickly intensified into a hurricane. After making landfall in North Carolina, it moved northeastward, transitioning into a post-tropical cyclone before reaching Atlantic Canada. Despite losing its tropical characteristics, Arthur maintained strong winds and heavy rainfall as it impacted the region.
Impact on Atlantic Canada
Arthur’s impact was most significant in Nova Scotia and New Brunswick. The storm caused widespread power outages, affecting over 250,000 homes and businesses. Trees were uprooted, and infrastructure such as power lines and roads was damaged. In New Brunswick, heavy rain led to flooding in several areas, while coastal regions experienced rough seas and high waves.
Response and Aftermath
The response to Hurricane Arthur involved extensive cleanup and restoration efforts, particularly focused on restoring power to affected areas. Emergency services were mobilized to address the damage, and recovery took several weeks. The storm prompted discussions about improving infrastructure resilience to withstand future storms.
Conclusion
Hurricane Arthur served as a reminder of the power of post-tropical storms and their potential to cause significant damage. The storm highlighted the need for ongoing preparedness and infrastructure improvements in Atlantic Canada.


